Describe the Relationship Between Detection Risk and Audit Risk
The risk that the auditors audit procedures will fail to detect a misstatement and the risk that the misstatements will get through the audit procedures. An auditor uses the audit risk model to understand the relationship between the detection risk and the other audit risks ie inherent risk control risk and the overall audit risk enabling him to determine an acceptable level of detection risk.
Difference Between Inherent Risk And Control Risk Difference Between
Detection risk is caused by the failure of the auditor to discover a.
. Estimating the inherent risk IR f. Inherent and control risk are the risks of material misstatement arising in the financial statements. For organisations without an effective enterprise risk management ERM function or one in its early stages of.
The auditor uses audit risk model to understand the relationship between detection risk and other risks in the audit risk model ie. It is composed of the possibility that 1 a material misstatement in an assertion about an account has occurred inherent risk and. For many years audit functions have used information about risk quite properly as one of the core inputs to audit planning.
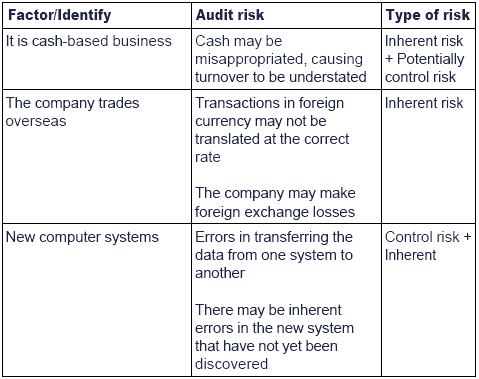
Auit risk Increases when we set our material at low level and Acceptable audit decreases when we set our materiality at higher leve. Identify and describe the two componentsof the risk of material misstatement. Conversely where the auditor believes the inherent and control risks of engagement to below detection risk is allowed to be set at a relatively.
As mentioned detection risk could be the result of poor audit planning. Distinguish among routine non-routineand estimation transactions. Describe the relationship between detection risk and audit risk.
Include an example of each. Detection risk is the risk that auditors fail to detect material misstatements that exist on the financial statements. View Homework Help - Hw 5 from ACCT 402 at California State University Fullerton.
Detection risk forms the residual risk after taking into consideration the inherent and control risks pertaining to the audit engagement and the overall audit risk that the auditor is willing to accept. Where the auditors assessment of inherent and control risk is high the detection risk is set at a lower level to keep the audit risk at an acceptable level. Describe the relationship betweendetection risk and audit risk.
Where the auditors assessment of inherent and control risk is high the detection risk is set at a lower level to keep the audit risk at an acceptable level. If the client shows a high detection risk the auditor will likely be able to detect any material errors. A certain amount of detection risk will always exist but the auditors goal is to lower the detection risk sufficiently for overall audit risk to maintain an acceptable level.
Detection risk is the risk that audit evidence Evidence in an Audit Evidence in an audit is information that is collected and required in the review of an entitys financial transactions balances and internal for any given audit assertion will fail to capture material misstatements. Audit risk refers to the possibility that the auditor may unknowingly fail to appropriately modify their opinion on financial statements that are materially misstated. The inherent risk control risk and overall audit risk.
Audit risk is a combination of three elements inherent Risk Control Risk Detection risk. On the other hand detection risk is the risk that is dependent entirely on the auditors. Identify and describe the two components of the risk of material misstatement.
These elements of the audit risk model are noted below. Level of materiality directly affect out acceptable level of audit risk. Can the auditorsreduce inherent risk by performing audit procedures.
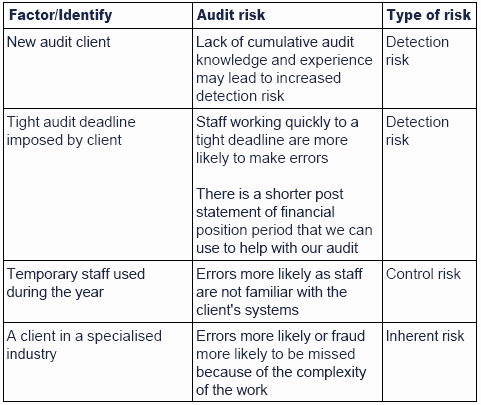
Factors Affecting Detection Risk. Principles of Auditing and Other Assurance Services with ACL Software CD 18th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 1RQ. Although detection risk cant be eliminated totally the auditor can manipulate it by modifying certain factors including.
Like audit risk detection risk does not assess detection risk rather it makes auditors seek to restrict it through the performance of substantive procedures Identify and describe the two components of the risk of material misstatement. Principles of Auditing Other Assurance Services 21st Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 1RQ. This note addresses the relationship between internal audit and risk management functions in organisations.
5-1 Describe the relationship between detection risk and audit risk. These types of audit risk are dependent on the business transactions and internal control system that the client has in place. This is due to without proper assessment of inherent and control risk auditors would have no basis for assessing the detection risk.
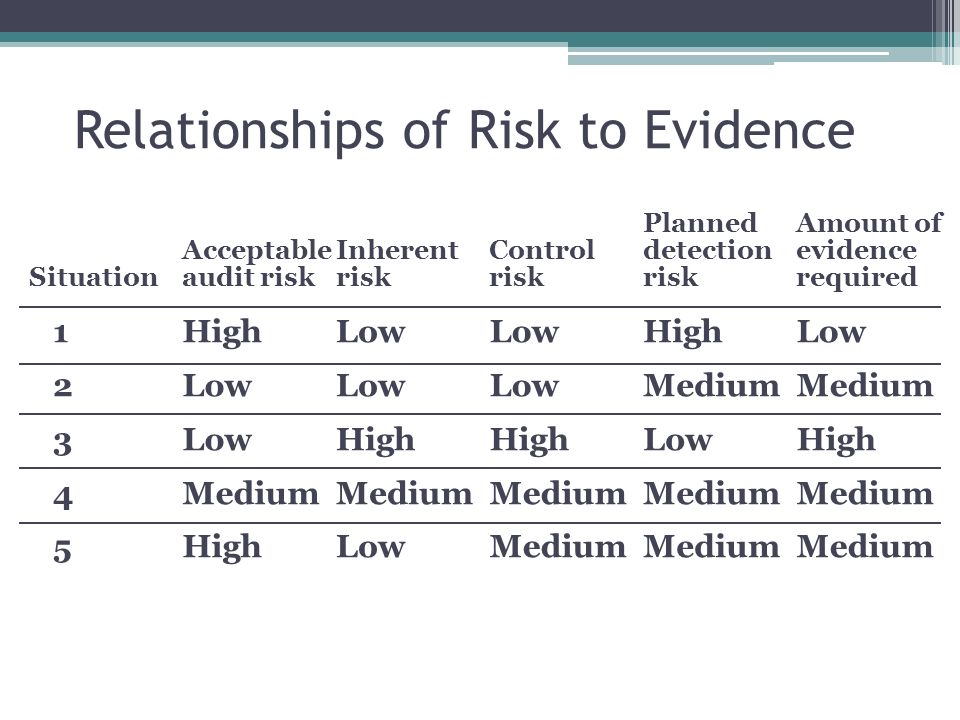
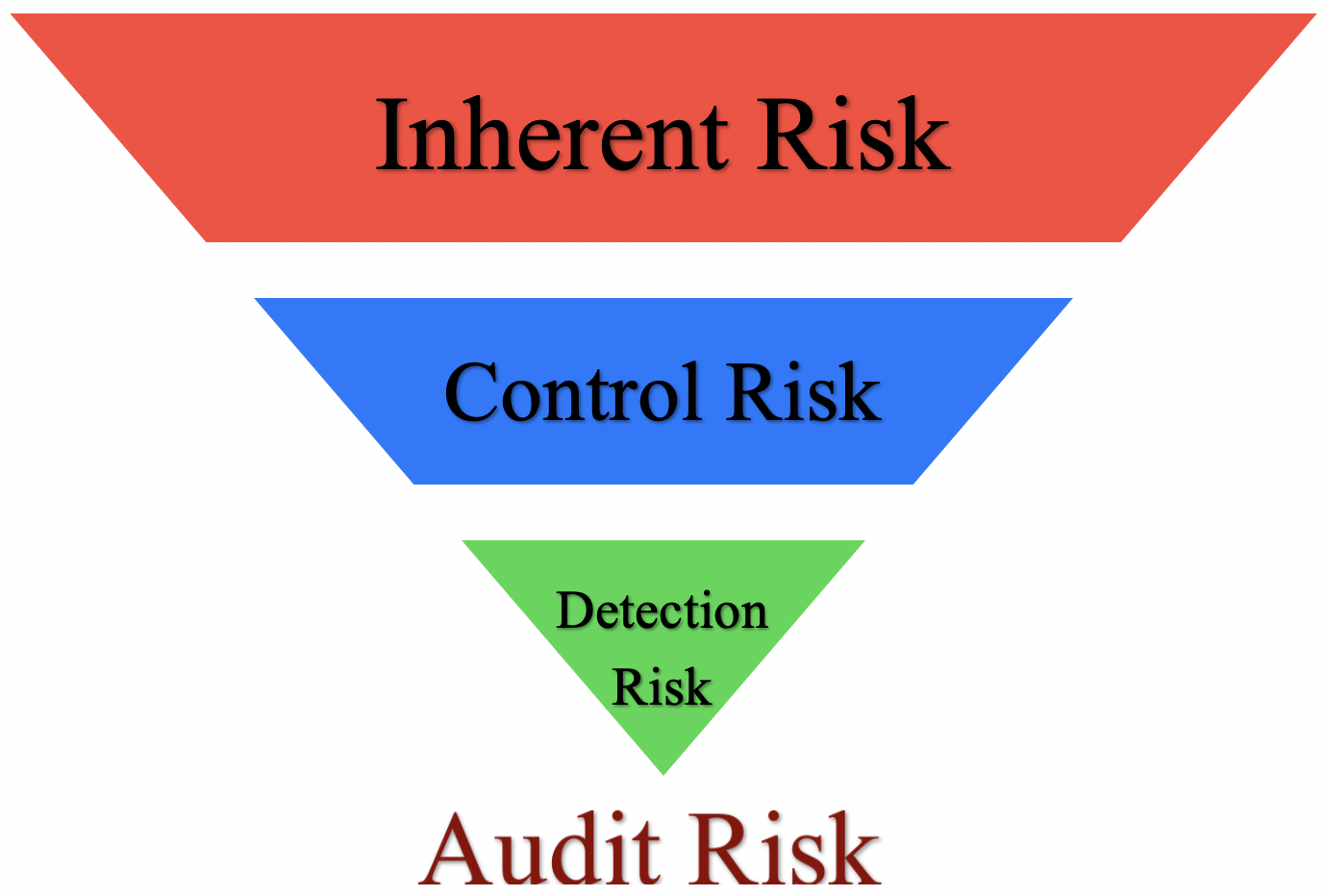
Defi ne inherent risk. Audit risk Control risk x Detection risk x Inherent risk. Proper understand will not only differentiate between different kinds of risks but also help you in recognizing the duties of management and auditor in a given context and the nature of their responsibilities.
Answer of 1. Describe the relationship between detection risk and audit risk. Control risk is caused by the failure of existing controls or the absence of controls leading to incorrect financial statements.
For a specified level of audit risk there is an inverse relationship between the assessed levels of inherent and control risks for an assertion and the level of risk that the auditor can accept that assertion. Even though detection risk cannot be eliminated entirely the auditor. The common cause of detection risk is improper audit planning poor engagement management wrong audit methodology low competency and lack of understanding of audit clients.
Solutions for problems in chapter 5. Describe the relationship between detection risk and audit risk. In risk based audit engagements understanding different kinds of risk become extremely important.
Detection risk is considered the last one of the three audit risk components. Detection risk is occurred because of the auditor part rather than the client part. Thus the lower the assessments of inherent and control risks the higher is the acceptable level of detection risk.
This enables the auditor to determine an acceptable level of detection risk. Describe the relationship between detection risk and audit risk. Describe the relationship between detection risk and audit risk.
Lower detection risk may be achieved by increasing the sample size for audit testing. DETECTION RISK EVIDENCE ACCUMULATION 3 D THE AUDIT RISK MODEL IN PRACTICE 5 This is defined in AUS 402 as the susceptibility of an account balance to misstatement that could be material assuming there were no related internal controls AUS 40209.
Advanced Auditing Materiality And The Audit Risk Model Ppt Download

Audit Risk Model Overview Risk Types Audit Assurance

What Is The Relationship Between Audit Risk And Materiality Universal Cpa Review

Qualitative Assessment Of Detection Risk In Audit 5 Control Risk Download Table

Three Components Of Audit Risk Download Scientific Diagram
Difference Between Inherent Risk And Control Risk Difference Between

Audit Risk And Business Risk Ppt Video Online Download

How Is Audit Risk Impacted With Changes In The Assessment Of Inherent Risk Control Risk And Detection Risk Universal Cpa Review

Three Components Of Audit Risk Download Scientific Diagram

Chapter 4 Audit Risk Business Risk And Audit Planning Ppt Download
3 Types Of Audit Risk Inherent Control And Detection Accountinguide

Solved Define The Terms Inherent Risk Control Risk Audit Risk Chegg Com

Audit Risk The Possibility That The Auditors May Unknowingly Fail To Appropriately Modify Their Opinion On Financial Statements That Are Materially Misstated Ppt Video Online Download




Comments
Post a Comment